HomeLab
- Architecture
- Création et configuration du serveur Proxmox
- Création d'un cluster K8S sur proxmox
- Création d'un cluster k3s mono-noeud sur Rocky Linux
- Déploiement de AWX
- Installation de forgejo sur rocky-linux en mode binaire
- Outils à suivre
Architecture
Architecture cible envisagée
Principe du Homelab Ops
Le principe du homelab que je souhaite mettre en place est la mise en place d'un outillage standard utilisé par une équipe Ops pour la gestion du "Build" et du "Run" d'un SI.
Etape 1 - Choix du matériel
Etape 2 - Choix de l'hyperviseur
Pour porter l'outillage, il est nécéssaire dans un premier temps d'avoir une couche de virtualisation et d'ochestration de container. Le choix s'est porté sur Proxmox pour plusieurs raisons:
- solution d’orchestration reconnue
Etape 3 - Mise en place de l'outillage
Etape 4 - Et si on jouait avec Kubernetes
Création et configuration du serveur Proxmox
Autorisation des VMS du réseau interne à aller sur internet (mode NAT)
Sur le server Proxmox, effectuer les opération suivantes
- Activer dans un des fichiers de conf sysctl "/etc/sysctl.d/99-xxx.conf" le forward IP.
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1- Créer les règles de NAT via iptable
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eno1 -j MASQUERADE
iptables -A FORWARD -i vmbr0 -j ACCEPT- Sauvegarder la configuration iptables dans "/etc/default/iptables"
iptables-save > /etc/default/iptables- Créer le fichier "/etc/network/if-pre-up.d/iptables" pour recharger le configuration iptables lors du reboot
#!/bin/sh
/usr/sbin/iptables-restore- Le rendre éxécutable
chmod +x /etc/network/if-pre-up.d/iptablesInstallation d'un HaProxy sur le serveur Proxmox pour proxifier les VMs
Installer HaProxy
apt install haproxyCréation d'un cluster K8S sur proxmox
Création de 3 VMS en désactivant le SWAP
- $ free -h.
- $ sudo swapoff -a.
- $ sudo nano /etc/fstab.
- # /dev/sda3 none swap sw 0 0.
- $ sudo swapoff -a.
Installation des outils
-
Update the
aptpackage index and install packages needed to use the Kubernetesaptrepository:sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gpg -
Download the public signing key for the Kubernetes package repositories. The same signing key is used for all repositories so you can disregard the version in the URL:
curl -fsSL https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.29/deb/Release.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg
/etc/apt/keyrings does not exist by default, and it should be created before the curl command.-
Add the appropriate Kubernetes
aptrepository. If you want to use Kubernetes version different than v1.29, replace v1.29 with the desired minor version in the command below:echo 'deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg] https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.29/deb/ /' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list before running apt-get update and apt-get upgrade. This procedure is described in more detail in Changing The Kubernetes Package Repository.-
Update
aptpackage index, then install kubectl:sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y docker.io kubelet kubeadm kubectl kubernetes-cni
containerd config default | sudo tee /etc/containerd/config.toml >/dev/null 2>&1
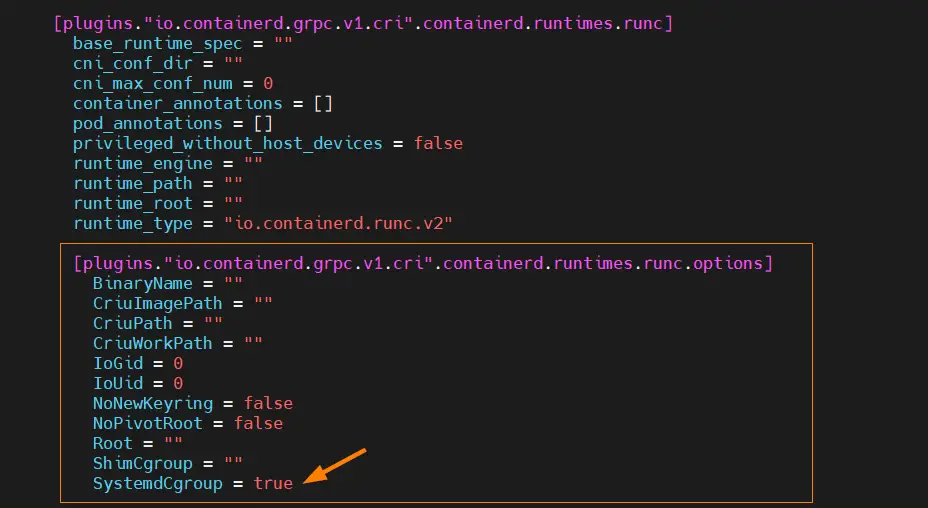
Edit the file ‘/etc/containerd/config.toml’ and look for the section ‘[plugins.”io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri”.containerd.runtimes.runc.options]’ and change ‘SystemdCgroup = false’ to ‘SystemdCgroup = true‘
$ sudo vi /etc/containerd/config.toml
Save and exit the file.
reboot
Initialisation du kube
Sur le noeud 1
kubeadm init
To start interacting with cluster, run following commands on master node,
$ mkdir -p $HOME/.kube $ sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config $ sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Run following kubectl command to get nodes and cluster information,
$ kubectl get nodes $ kubectl cluster-info
Output of above commands
Ajout de nodes dans le kube
Création d'un cluster k3s mono-noeud sur Rocky Linux
Mise en place des pré-requis
Désactiver firewalld
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalldDésactiver selinux en modifiant le fichier /etc/sysconfig/selinux
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
# See also:
# https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/9/html/using_selinux/changing-selinux-states-and-modes_using-selinux#changing-selinux-modes-at-boot-time_changing-selinux-states-and-modes
#
# NOTE: Up to RHEL 8 release included, SELINUX=disabled would also
# fully disable SELinux during boot. If you need a system with SELinux
# fully disabled instead of SELinux running with no policy loaded, you
# need to pass selinux=0 to the kernel command line. You can use grubby
# to persistently set the bootloader to boot with selinux=0:
#
# grubby --update-kernel ALL --args selinux=0
#
# To revert back to SELinux enabled:
#
# grubby --update-kernel ALL --remove-args selinux
#
SELINUX=disabled
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these three values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targetedInstaller les packages manquants suivants
dnf install -y git tar bash-completionModifier les paramètres kernel suivants en créant le fichier /etc/sysctl.d/99-tunning.conf
#Disable IP V6
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1
#tunning fs
fs.aio-max-nr = 1048576
fs.file-max = 6815744
#Limit Swap
vm.swappiness = 10
vm.max_map_count = 262144
vm.overcommit_memory = 1
net.core.somaxconn=65535
#Tuning IPV4
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 10000 65500
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time=30
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvl=30
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probes=10Rebooter le server
Installation de kubectl et d'un kube k3s
Installation de kubectl
Télécharger le binaire kubectl et le déposer dans /usr/local/bin/
curl -LO https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -Ls https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
chmod +x ./kubectl
sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectlModifier le bashrc pour ajouter /usr/local/bin dans la variable $PATH
...
...
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/bin
...Ajouter la completion sur kubectl
echo 'source <(kubectl completion bash)' >>~/.bashrcVérifier que le binaire est opérationnel
kubectl version --clientInstallation de K3S sans le composant “Traeffik” et en choisissant un CIDR qui n'overlap pas un réseau existant
curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | K3S_KUBECONFIG_MODE="644" INSTALL_K3S_EXEC="--cluster-cidr=192.168.255.0/24 --disable=traefik" sh -A la fin du déploiement, créer le fichier d'authentification / connection au cluster kubernetes pour le client kubectl
mkdir ~/.kube
cp /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml ~/.kube/configVérifier que le kube est correctement démarrer
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system coredns-0587-fbcd5-sdfsf 1/1 Running 0 84s
kube-system local-path-provisioner-fdsfsfs-r6pbm 1/1 Running 0 84sDéploiement de AWX
Installation de awx
Les prérequis suivant sont nécéssaires
kubectl est installé et configuré pour se connecter à un cluster kubernetes
Création du dossier d'installation
mkdir ~/install-awxCréer le fichier ~/install-awx/kustomization.yaml pour déployer la dernière version de awx-operator
- Remplacer la valeur 2.18.0 par la dernière version disponible : https://github.com/ansible/awx-operator
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
# Find the latest tag here: https://github.com/ansible/awx-operator/releases
- github.com/ansible/awx-operator/config/default?ref=2.18.0
- awx-deploy.yml
# Set the image tags to match the git version from above
images:
- name: quay.io/ansible/awx-operator
newTag: 2.18.0
# Specify a custom namespace in which to install AWX
namespace: awxDéployer awx-operator
cd ~/install-awx/
kubectl apply -k .Création du fichier ~/install-awx/awx-deploy.yml
---
apiVersion: awx.ansible.com/v1beta1
kind: AWX
metadata:
name: awx
spec:
service_type: nodeportLancer l'installation de awx
cd ~/install-awx/
kubectl apply -k .Suivre le déploiement en regardant les logs de déploiement
kubectl logs -f deployments/awx-operator-controller-manager -c awx-manager -n awxA la fin du déploiement vérifier que les 4 pods sont déployés
kubectl get pods -n awx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
awx-postgres-13-0 1/1 Running 2 (2d20h ago) 3d13h
awx-operator-controller-manager-66c5b94884-l8hkk 2/2 Running 6 (2d20h ago) 3d13h
awx-task-5c97798797-5q8tn 4/4 Running 8 (2d20h ago) 3d13h
awx-web-7fcd58c7b9-md59b 3/3 Running 6 (2d20h ago) 3d13hRécupération des informations utiles
Récupérer le port exposé en local du service awx pour le proxifier/exposer par la suite
- Dans l’exemple ci-dessous le port exposé est le port TCP 32524 qui expose le port interne 80
kubectl get service awx-service -n awx
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
awx-service NodePort 10.43.29.126 <none> 80:32524/TCP 3d13hRécupérer le mot de passe du compte “admin” présent dans le secret “awx-admin-password” via la commande suivante
kubectl get secret awx-admin-password -o go-template='{{range $k,$v := .data}}{{printf "%s: " $k}}{{if not $v}}{{$v}}{{else}}{{$v | base64decode}}{{end}}{{"\n"}}{{end}}' -n awxMise à jour de awx
Modifier le fichier ~/install-awx/kustomization.yaml pour déployer la dernière version de awx-operator
- Remplacer la valeur 2.18.0 par la dernière version disponible : https://github.com/ansible/awx-operator
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
# Find the latest tag here: https://github.com/ansible/awx-operator/releases
- github.com/ansible/awx-operator/config/default?ref=2.18.0
- awx-deploy.yml
# Set the image tags to match the git version from above
images:
- name: quay.io/ansible/awx-operator
newTag: 2.18.0
# Specify a custom namespace in which to install AWX
namespace: awxExécuter les commandes suivantes pour mettre à jour awx
kubectl delete deployment awx-operator-controller-manager -n awx
kubectl delete serviceaccount awx-operator-controller-manager -n awx
kubectl delete rolebinding awx-operator-awx-manager-rolebinding -n awx
kubectl delete role awx-operator-awx-manager-role -n awx
cd ~/install-awx/
kubectl apply -k .Installation de forgejo sur rocky-linux en mode binaire
Installation des pré-requis
Installation des packages manquants
dnf install -y git git-lfs wgetInstallation de mariadb-server
Installer le package mariadb-server
dnf install -y mariadb-serverActiver et démarrer le service mariadb
systemctl enable mariadb
systemctl start mariadbCréer la base de données forgejo et l'utilisateur associé
create database forgejo CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
grant all privileges on forgejo.* TO 'forgejo'@'127.0.0.1' identified by 'PASSWORD';
flush privileges;Installation de forgejo
Création du groupe et du user associé au futur service
groupadd --system git
adduser --system --shell /bin/bash --comment 'Git Version Control' --gid git --home-dir /home/git --create-home gitCréation des dossiers qui seront utilisés par le service
- Création du dossier /var/lib/forgejo qui contiendra les données
mkdir /var/lib/forgejo
chown git:git /var/lib/forgejo && chmod 750 /var/lib/forgejo- Création du dossier /etc/forgejo qui contiendra le fichier de configuration app.ini
mkdir /etc/forgejo
chown root:git /etc/forgejo && chmod 770 /etc/forgejoRecuperation du binaire forgejo
cd /usr/local/bin
wget https://codeberg.org/forgejo/forgejo/releases/download/v7.0.4/forgejo-7.0.4-linux-amd64
chmod 755 /usr/local/bin/forgejo-7.0.4-linux-amd64
ln -s forgejo-7.0.4-linux-amd64 forgejoInstallation du service
wget -O /etc/systemd/system/forgejo.service https://codeberg.org/forgejo/forgejo/raw/branch/forgejo/contrib/systemd/forgejo.serviceOuverture firewall du port tcp/3000 sur firewalld
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3000/tcp
firewall-cmd --reloadDémarrage du service forgejo
systemctl enable forgejo.service
systemctl start forgejo.serviceOutils à suivre
https://github.com/D10S0VSkY-OSS/Stack-Lifecycle-Deployment
Registry Docker
Solution GitOps
- ArgoCD : https://argoproj.github.io/cd/
- Flux : Flux (fluxcd.io)
- Kargo : GitHub - akuity/kargo: Application lifecycle orchestration